transparent
2. 근본적인 문제해결은 BitBlt 함수를 이용해 새로운 함수를 설계하는 것이다. ¶SUMMARY
''A portion of a graphic image that does not change the contents of the screen is termed "transparent." The DrawIcon function can create an image that contains transparent portions. It is also possible to obtain this functionality using the BitBlt function; however, there are some additional steps involved.
The first step is to obtain the contents of the area where the bitmap will be drawn and to store this background image in a memory display context (DC). Mask out the area of the background that corresponds to the nontransparent portion of the image bitmap and mask out all transparent pixels from the image bitmap. Use the XOR raster operation to merge the image bitmap into the background bitmap. Finally, use the BitBlt function to move the merged image to the destination DC.''
요약
DrawIcon 함수는 부분적으로 투명한 이미지를 생성할 수 있다. 이것은 BitBlt함수로 투명한 이미지를 생성할 수 있는 가능성을 가질 수 있다.
계속해서, 우선 투명한 비트맵이 그려질 배경 비트맵이 그려진 메모리 DC를 생성한다.
이제 배경 비트맵과 투명하게 설정된(컬러키) 부분을 제외한 비트맵을 합성한다.
그 방법은 두 이미지에 XOR 래스터 연산을 사용한다.
끝으로 DC에 합병된 이미지를 블리팅한다.
(위 문단과 문단 위의 영문단은 꼭 같은 내용이 아님)
3. 문제 해결을 위한 세부적인 함수 설계 방법. ¶알림. 투명한 부분을 가진 비트맵은 컬러키를 통해 준비한다.
알림2. 투명한 부분을 가진 비트맵은 이하 투명 비트맵으로한다.
단계 1) 준비 단계
1. 배경 비트맵을 부착시킬 DC를 생성한다. (이하 배경 DC)
2. 배경 비트맵을 배경 DC에 부착시킨다.
3. 생성될 투명 비트맵을 부착시킬 메모리 DC를 생성한다. (이하 메모리 DC)
4. 투명 비트맵이 부착될 배경 DC의 부분을 메모리 DC에 복사한다.
단계 2) 마스크 생성
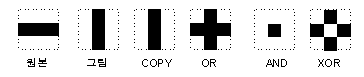
5. 그릴 부분을 포함하는 마스크를 생성한다.
5-1. 컬러키를 배경으로 가지는 DC를 생성한다. (이하 컬러키DC)
단계 3) 마스크 래스터 연산 작업
5-2. 투명 비트맵을 컬러키DC에 부착한다. (이 작업에서 투명비트맵의 투명한 부분이 배경색과 같다)
5-3. 흑백의 컬러만를 가진 DC를 생성한다. (이하 흑백DC)
5-4. 컬러키DC를 흑백DC로 복사한다. (이 작업에서 배경색은 흰색(값은 1)으로, 컬러키 이외의 색을 가진 부분은 검은색(값은 0)으로 변한다)
6. BitBlt 함수를 이용해 SRCAND 래스터 연산(A 마스크 & 메모리 DC)으로 A 마스크를 메모리 DC 위에 복사한다.
7. BitBlt 함수를 이용해 SRCAND 래스터 연산(나머지 부분 & 배경 DC)으로 A 마스크가 포함되지 않는 나머지 부분을 배경 DC 위에 복사한다.
8. BitBlt 함수를 이용해 SRCPAINT 래스터 연산(배경 DC | 메모리 DC)으로 배경 DC를 메모리 DC 위에 복사한다.
9. BitBlt 함수를 이용해 메모리 DC를 화면으로 전송한다.
단계 4) 메모리 해제
10. 할당된 메모리를 모두 해제한다.
(위 작업 방법과 MSDN의 영문단은 꼭 같은 내용이 아님, 이해 하기 쉽도록 각 이름을 명시하고 재 배열함)
참고) 래스터 연산
BitBlt 함수의 ROP의 인수로 다음 매크로들을 전송한다.
S는 Source D는 Destination를 뜻한다.
SRCAND 0x008800C6 S&D (Source and Destination)
SRCPAINT 0x00EE0086 S|D (Source or Destination)
 [GIF image (1.91 KB)] 이미지 출처: Win32 Api 연구사이트
4. 위의 방법으로 설계된 함수의 소스 코드 ¶
void DrawTransparentBitmap(HDC hdc, HBITMAP hBitmap, short xStart,
short yStart, COLORREF cTransparentColor)
{
BITMAP bm;
COLORREF cColor;
HBITMAP bmAndBack, bmAndObject, bmAndMem, bmSave;
HBITMAP bmBackOld, bmObjectOld, bmMemOld, bmSaveOld;
HDC hdcMem, hdcBack, hdcObject, hdcTemp, hdcSave;
POINT ptSize;
hdcTemp = CreateCompatibleDC(hdc);
SelectObject(hdcTemp, hBitmap); // Select the bitmap
GetObject(hBitmap, sizeof(BITMAP), (LPSTR)&bm);
ptSize.x = bm.bmWidth; // Get width of bitmap
ptSize.y = bm.bmHeight; // Get height of bitmap
DPtoLP(hdcTemp, &ptSize, 1); // Convert from device
// to logical points
// Create some DCs to hold temporary data.
hdcBack = CreateCompatibleDC(hdc);
hdcObject = CreateCompatibleDC(hdc);
hdcMem = CreateCompatibleDC(hdc);
hdcSave = CreateCompatibleDC(hdc);
// Create a bitmap for each DC. DCs are required for a number of
// GDI functions.
// Monochrome DC
bmAndBack = CreateBitmap(ptSize.x, ptSize.y, 1, 1, NULL);
// Monochrome DC
bmAndObject = CreateBitmap(ptSize.x, ptSize.y, 1, 1, NULL);
bmAndMem = CreateCompatibleBitmap(hdc, ptSize.x, ptSize.y);
bmSave = CreateCompatibleBitmap(hdc, ptSize.x, ptSize.y);
// Each DC must select a bitmap object to store pixel data.
bmBackOld = SelectObject(hdcBack, bmAndBack);
bmObjectOld = SelectObject(hdcObject, bmAndObject);
bmMemOld = SelectObject(hdcMem, bmAndMem);
bmSaveOld = SelectObject(hdcSave, bmSave);
// Set proper mapping mode.
SetMapMode(hdcTemp, GetMapMode(hdc));
// Save the bitmap sent here, because it will be overwritten.
BitBlt(hdcSave, 0, 0, ptSize.x, ptSize.y, hdcTemp, 0, 0, SRCCOPY);
// Set the background color of the source DC to the color.
// contained in the parts of the bitmap that should be transparent
cColor = SetBkColor(hdcTemp, cTransparentColor);
// Create the object mask for the bitmap by performing a BitBlt
// from the source bitmap to a monochrome bitmap.
BitBlt(hdcObject, 0, 0, ptSize.x, ptSize.y, hdcTemp, 0, 0,
SRCCOPY);
// Set the background color of the source DC back to the original
// color.
SetBkColor(hdcTemp, cColor);
// Create the inverse of the object mask.
BitBlt(hdcBack, 0, 0, ptSize.x, ptSize.y, hdcObject, 0, 0,
NOTSRCCOPY);
// Copy the background of the main DC to the destination.
BitBlt(hdcMem, 0, 0, ptSize.x, ptSize.y, hdc, xStart, yStart,
SRCCOPY);
// Mask out the places where the bitmap will be placed.
BitBlt(hdcMem, 0, 0, ptSize.x, ptSize.y, hdcObject, 0, 0, SRCAND);
// Mask out the transparent colored pixels on the bitmap.
BitBlt(hdcTemp, 0, 0, ptSize.x, ptSize.y, hdcBack, 0, 0, SRCAND);
// XOR the bitmap with the background on the destination DC.
BitBlt(hdcMem, 0, 0, ptSize.x, ptSize.y, hdcTemp, 0, 0, SRCPAINT);
// Copy the destination to the screen.
BitBlt(hdc, xStart, yStart, ptSize.x, ptSize.y, hdcMem, 0, 0,
SRCCOPY);
// Place the original bitmap back into the bitmap sent here.
BitBlt(hdcTemp, 0, 0, ptSize.x, ptSize.y, hdcSave, 0, 0, SRCCOPY);
// Delete the memory bitmaps.
DeleteObject(SelectObject(hdcBack, bmBackOld));
DeleteObject(SelectObject(hdcObject, bmObjectOld));
DeleteObject(SelectObject(hdcMem, bmMemOld));
DeleteObject(SelectObject(hdcSave, bmSaveOld));
// Delete the memory DCs.
DeleteDC(hdcMem);
DeleteDC(hdcBack);
DeleteDC(hdcObject);
DeleteDC(hdcSave);
DeleteDC(hdcTemp);
}
소스코드 및 상기 방법의 원본의 출처: http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;79212
익명, -- donguk22 2006-01-30 14:54:34
|
His heart was yours from the first moment that you met. |